Array
An array is a collection of similar data types that are stored in contiguous memory locations. Each location has an index number through which we can access the element at that particular index.
In programming, we often need to use data elements of similar type and purpose. Instead of declaring and defining every variable individually, we can use an array to store all of them together.
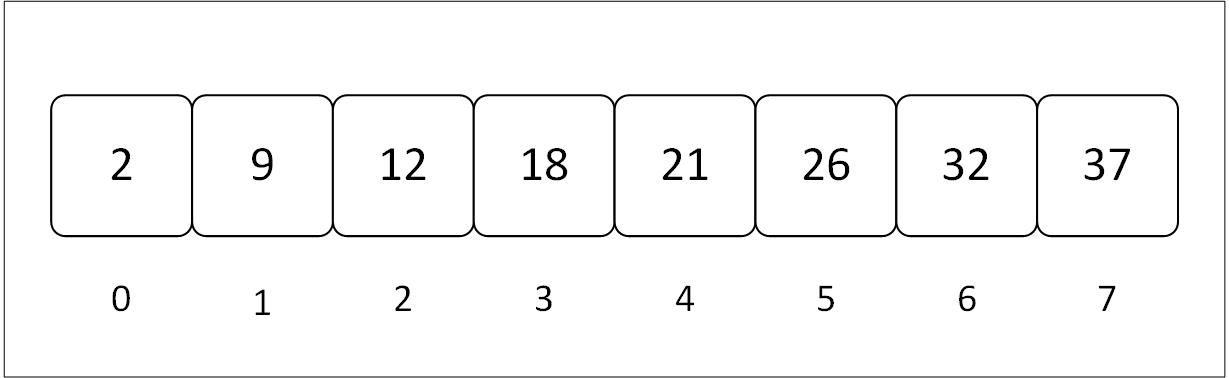
Figure 3.1: Visual representation of an array with contiguous memory and indices
The array in the diagram has 8 elements, and hence we say its size is 8 (length in terms of Rust).
The line of numbers below the array is called the indices of the array. These numbers are the addresses of elements in the array. We access elements with the help of these numbers. An index number generally starts with 0.
For instance, if you want to access the 4th element, you'll do that by its index, i.e., 4 - 1 = 3:
number = array[3];
In Rust, an array can be defined in two methods. Each method comes with its pros and cons. The two types of arrays in Rust are: Primitive type and Vector type.
Array Algorithms
These algorithms, while not specific to the array data type, serve an important function when dealing with them. While we don't need algorithms to traverse, access, or insert elements in arrays like we will in other data structures, there are some functionalities that require different algorithms.
Search Algorithms 🔍
They serve the function of checking and retrieving information stored within some data structure where that data is stored.
1. Linear Search algorithm: It is also called a sequential search algorithm. This algorithm works by sequentially iterating through the whole array from one end until the target element is found. If found, the algorithm returns its index; else -1.
2. Binary Search Algorithm: This type of searching algorithm is used to find the position of a specific value contained in a sorted array. The binary search algorithm works on the principle of divide and conquer and is the best searching algorithm because it is faster to run.
Sorting Algorithms 🧲
Sorting algorithms rearrange a given array of elements in a specific order. In the case of numbers, it could be ascending or descending order.
1. Bubble Sort: It is the simplest sorting algorithm, where it iteratively swaps the adjacent elements if they are in the wrong order.
2. Selection Sort: This algorithm works by iteratively selecting the smallest/largest element from the unsorted portion of the list and moving it to the sorted portion of the array.
3. Insertion Sort: This sorting algorithm works by iteratively inserting each element of an unsorted array into its correct position in a sorted portion of the list.
4. Merge Sort: It is a sorting algorithm that follows the divide and conquer strategy. It works by iteratively dividing the input array into smaller sub-arrays and sorting those sub-arrays, then merging them back together to obtain the sorted array.
5. Quick Sort: It is a sorting algorithm that implements the divide and conquer strategy and picks an element as a pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot by placing the pivot in its correct position in the sorted array.
We'll learn how to implement these algorithms after we have understood what arrays are.