Queue
A queue is a linear data used to model a First In First Out (FIFO) system. Conceptually, we add elements to the end of the queue and remove elements from the front.
The queue is used to model a system where the order of elements is important. For example, in a print queue, the order of jobs is important, so we use a queue to manage the jobs.
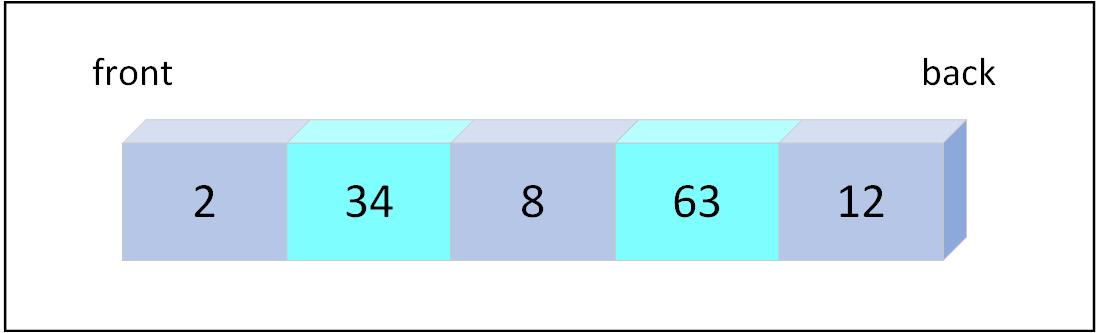
Figure 6.1: Visual representation of a queue
In Rust, we use a VecDeque to implement a queue. The VecDeque is a double-ended queue that allows efficient insertion and removal at both ends. It is a wrapper around a Vec that provides additional methods for working with the queue.
Operations
To import the VecDeque type, we need to add the following line at the top of our file:
use std::collections::VecDeque;Enqueue
Enqueue is the operation of adding an element to the end of the queue. The push_back method is used to add an element to the back of the queue.
// Enqueue operation
queue.push_back(2);
queue.push_back(34);
queue.push_back(8);
queue.push_back(63);
queue.push_back(12);Dequeue
Dequeue is the operation of removing an element from the front of the queue. The pop_front method is used to remove an element from the front of the queue.
// Dequeue operation
let popped = queue.pop_front();
println!("Popped value: {}", popped.unwrap());Peek
Peek is the operation of viewing the element at the front of the queue without removing it. The front method is used to view the element at the front of the queue.
// Peek operation
let front = queue.front();
println!("Front value: {}", front.unwrap());Result
use std::collections::VecDeque; fn main() { let mut queue = VecDeque::new(); // Enqueue operation queue.push_back(2); queue.push_back(34); queue.push_back(8); queue.push_back(63); queue.push_back(12); println!("Queue: {:?}", queue); // Dequeue operation let popped = queue.pop_front(); println!("Popped value: {}", popped.unwrap()); // Peek operation let front = queue.front(); println!("Front value: {}", front.unwrap()); }